Think Bitcoin is untraceable? Think again.
Every Bitcoin transaction leaves a digital footprint. Investigators, hackers, and even governments can track your Bitcoin transaction history—sometimes all the way back to your identity. The blockchain doesn’t forget.
But does that mean privacy is impossible? Not exactly. While Bitcoin is traceable, there are ways to stay under the radar. The key is knowing how the system works—and how to outsmart the tools used to track it.
Let’s break down the truth about Bitcoin anonymity, how transactions are traced, and what you can do to protect your privacy.
Is Bitcoin anonymous or traceable?
Is Bitcoin traceable or anonymous? The answer is both. It offers pseudonymity, not full privacy.
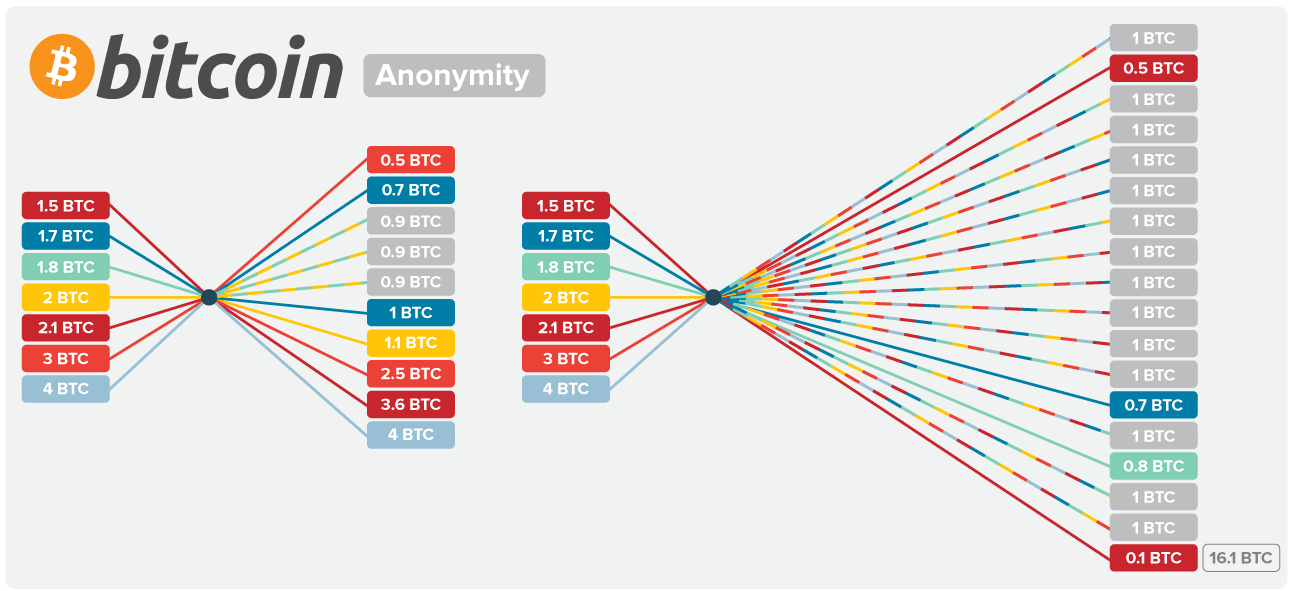
Bitcoin is often called anonymous, but that’s not exactly true. While it doesn’t require your name or ID to send or receive funds, every transaction is recorded on a public ledger. This means Bitcoin is traceable to anyone—if they know where to look.
Why Bitcoin’s pseudonymity works
Bitcoin doesn’t use personal information like banks do. Instead, transactions are tied to wallet addresses. These long strings of numbers and letters don’t reveal a real-world identity. This setup makes Bitcoin pseudonymous, but not private.
Once a wallet address is linked to you, all its transactions become traceable. If you’ve ever used an exchange that requires ID verification or sent Bitcoin to someone who knows you, your anonymity is compromised.
Every transaction includes a Bitcoin transaction ID (TXID), which can be tracked on the blockchain forever. With the right tools, investigators can follow the money.
Why Bitcoin transactions are public
Bitcoin’s blockchain is designed for transparency. Every transaction is permanently recorded, and anyone can check the entire Bitcoin transaction history at any time.
This openness ensures no one can alter or fake transactions, which is great for security—but bad for privacy. Unlike cash, your Bitcoin transaction history leaves a permanent digital trail.
Blockchain forensic firms use Bitcoin forensic analysis to track these transactions. They can uncover real identities by analyzing patterns, linking wallet addresses, and cross-referencing data from exchanges.
Common misconceptions about Bitcoin privacy
- Bitcoin is completely anonymous: Not true. Bitcoin is traceable back to wallet addresses and real-world identities.
- If I don’t use my real name, no one can track me: Even if your name isn’t attached, your transaction history is public. If an address gets linked to you, everything is exposed.
- Privacy wallets and mixers make Bitcoin untraceable: While tools like CoinJoin and Bitcoin mixers help obscure transactions, they don’t make Bitcoin untraceable. Forensic analysts still have ways to de-anonymize mixed funds.
- Using a VPN or Tor makes Bitcoin transactions anonymous: These tools hide your IP address to give you more privacy, but they don’t erase your transaction trail. Your Bitcoin transaction ID is still visible on the blockchain.
How Bitcoin transactions are traced
Bitcoin’s wallet addresses don’t contain personal details, but blockchain analysis techniques can reveal patterns that help investigators trace transactions.
Blockchain analysis techniques
Blockchain analysis means examining Bitcoin transaction history to identify connections between wallets and individuals. Specialized firms and law enforcement agencies use advanced tools to map out Bitcoin flows and track suspicious activity.
Some of the most common techniques include:
- Transaction clustering: Analyzing patterns to group multiple wallet addresses that likely belong to the same person or organization.
- Heuristic analysis: Identifying behaviors that reveal connections, such as spending patterns or repeated transactions to the same addresses.
- Address tagging: Linking Bitcoin addresses to known entities like exchanges, darknet markets, or ransomware groups.
- TXID tracking: Following Bitcoin transaction IDs to trace funds through the blockchain.
These methods allow analysts to track Bitcoin movements—even when people try to stay anonymous.
How investigators connect addresses to real identities
A Bitcoin wallet address alone doesn’t reveal a person’s identity. But when combined with external data, it’s possible to unmask the person behind a transaction. Here’s how:
- Exchange KYC data: Many crypto exchanges require users to verify their identity before trading. If a traced Bitcoin address is linked to an exchange, investigators can request user data.
- IP address tracking: If someone doesn’t mask their IP address while making a transaction, it can be logged and used to identify them.
- Withdrawal patterns: If Bitcoin is withdrawn to a bank account or another payment method, it creates a clear link to a real-world identity.
- Blockchain forensic databases: Some companies maintain large databases of known Bitcoin addresses, helping investigators match wallets to individuals or businesses.
Real-world examples of Bitcoin tracking
Bitcoin tracking isn’t just theoretical—it’s been used to solve major criminal cases and uncover hidden transactions. Here are a few notable examples:
- Silk Road takedown: The FBI traced Bitcoin transactions from the infamous darknet market, leading to the arrest of its founder, Ross Ulbricht.
- Colonial Pipeline ransomware: U.S. authorities recovered millions in Bitcoin ransom payments by tracking transactions on the blockchain.
- IRS crypto tax enforcement: The IRS has used blockchain analysis tools to identify and prosecute people who failed to report crypto income.
Clearly, Bitcoin is traceable, and even criminals who try to hide their tracks can be caught.
Why Bitcoin’s transparency matters
Bitcoin’s open ledger is one of its defining features. Every transaction is permanently recorded. This transparency is a double-edged sword—it helps prevent fraud and ensures accountability, but it also means your transactions are never truly private.
Benefits of a transparent blockchain
Bitcoin’s public ledger has key advantages, making it more reliable than traditional financial systems in many ways:
- Prevents double spending: Since all transactions are recorded, no one can spend the same Bitcoin twice.
- Eliminates the need for trust: Unlike banks, which require trust in third parties, Bitcoin’s blockchain allows anyone to verify transactions directly.
- Improves security: The decentralized nature of Bitcoin makes it resistant to fraud, censorship, and tampering.
- Enables financial auditing: Businesses and organizations can use Bitcoin for transparent accounting, ensuring accountability without relying on third parties.
- Supports law enforcement investigations: Authorities can track stolen or illicit funds, making it harder for criminals to launder money.
Risks of traceable transactions
Transparency helps maintain Bitcoin’s integrity, but it also creates risks for people who value privacy.
- Loss of financial privacy: Bitcoin payments are permanently recorded. This means Bitcoin is traceable, allowing anyone to track your spending habits.
- Exposure to surveillance: Governments, corporations, and cybercriminals can monitor transactions and link them to real identities.
- Potential for censorship: If authorities or financial institutions blacklist certain wallet addresses, those funds can become unusable.
- Increased risk of hacking: If your Bitcoin address is publicly known, you could become a target for cybercriminals looking to reveal your identity and steal funds.
- Compromised anonymity: If someone can link your wallet address to your identity, they can trace your entire Bitcoin transaction history.
For those who want untraceable crypto, Bitcoin’s public ledger is a major drawback. If you’re not careful, you could lose your financial privacy—or even access to your funds.
How Bitcoin traceability impacts users
Bitcoin’s traceability affects different people in different ways, depending on how they use it.
- Everyday users: People who make purchases with Bitcoin may unknowingly expose their entire transaction history if their wallet address is linked to their identity.
- Privacy advocates: If you want anonymous payment methods, take extra precautions to avoid being tracked.
- Businesses: Companies accepting Bitcoin must consider the transparency of their transactions, especially when handling customer payments.
- Criminals: While some assume Bitcoin is untraceable, law enforcement has proven otherwise by tracking and seizing illicit funds.
- Tax authorities: The IRS and other agencies use Bitcoin forensic analysis to track undeclared crypto income and enforce tax regulations.
Privacy tools to enhance Bitcoin anonymity
If you don’t want your Bitcoin transaction history to be publicly linked to your identity, privacy tools can help obscure your activity.
How Conjoin works
CoinJoin is a Bitcoin mixing technique that combines multiple transactions into one, making it harder to track where funds come from and where they go.
Here’s how it works:
- Multiple people send Bitcoin into a single, large transaction.
- The transaction is broken down and sent to different output addresses.
- Since the outputs are mixed, it’s difficult to tell which Bitcoin belongs to whom.
CoinJoin obscures transaction history to make Bitcoin transactions harder to trace. However, forensic tools can sometimes identify CoinJoin transactions, so it doesn’t guarantee full anonymity.
The role of Bitcoin mixers
Bitcoin mixers are often called tumblers. They shuffle Bitcoin between multiple wallets to break the link between the sender and receiver.
There are two main types:
- Centralized mixers: These services take Bitcoin from users, mix it with other funds, and send back new coins with no direct link to the original transaction.
- Decentralized mixers: These use smart contracts or peer-to-peer mixing to achieve the same goal without a central authority.
Mixers make it harder to track Bitcoin movements, but they come with risks. Many centralized services require trust in the provider, and some have been shut down or seized by law enforcement. Using a decentralized Bitcoin mixer offers better privacy, but forensic techniques can still identify certain patterns.
Using privacy wallets to reduce traceability
Privacy-focused Bitcoin wallets offer built-in features that help make transactions harder to trace. Some of the most popular options include Wasabi Wallet, which uses CoinJoin, and Samourai Wallet, which includes tools like Whirlpool and Ricochet. If you’re looking for a secure mobile option, check out the best Bitcoin wallet for iOS.
Some of the most popular privacy wallets include:
- Wasabi Wallet: Uses CoinJoin to mix transactions automatically.
- Samourai Wallet: Includes features like Whirlpool (a CoinJoin implementation) and Ricochet (which adds extra hops to transactions to confuse tracking).
- Electrum with CoinJoin: A lightweight Bitcoin wallet that allows users to mix transactions for better privacy.
These wallets help break the link between your Bitcoin addresses and transaction history, reducing the risk of being tracked. However, they’re not foolproof—if you reuse addresses, interact with exchanges, or fail to take additional privacy precautions, your transactions can still be traced.
To improve privacy, avoid reusing wallet addresses and use privacy tools like CoinJoin, Bitcoin mixers, and stealth addresses. The Lightning Network can also help by keeping transactions off the main blockchain. For added security in online transactions beyond Bitcoin, consider using a VPN for PayPal to protect your financial data in transit.
Bitcoins vs. privacy coins: Which is more anonymous?
Every transaction leaves a digital footprint that anyone can analyze. This has led to the rise of privacy coins—cryptocurrencies designed to keep financial activity hidden.
Public cryptocurrencies vs. privacy coins
Most cryptocurrencies operate on transparent blockchains, where transaction details are permanently visible. Privacy coins are different. These are built with advanced encryption to make tracing transactions significantly harder.
Instead of recording clear transaction paths like Bitcoin does, privacy-focused cryptocurrencies use techniques that hide wallet addresses, transaction amounts, or both.
Here’s how they differ:
- Bitcoin: Transactions are recorded in a way that allows tracking, even if the sender and receiver aren’t directly identified.
- Privacy coins: Use cryptographic methods to mask transaction details, making it very difficult to trace funds.
How Monero and Zcash provide better anonymity
Monero and Zcash are two of the most well-known privacy coins, each offering stronger anonymity than Bitcoin.
Monero is designed so that all transactions are private by default. It achieves this through:
- Ring signatures: Grouping multiple possible senders in a single transaction, making it unclear who actually sent the funds.
- Stealth addresses: Generating unique, one-time addresses for each transaction, hiding the recipient’s real wallet.
- RingCT (Ring Confidential Transactions): Obscuring transaction amounts so that no one can see how much was sent.
Because Monero’s blockchain conceals all key transaction details, it’s nearly impossible to track.
Zcash offers selective privacy through its zk-SNARKs encryption, which verifies transactions without revealing any details. Zcash users can choose between:
- Transparent transactions: Similar to Bitcoin, with full public visibility.
- Shielded transactions: Fully encrypted, hiding the sender, receiver, and amount.
Zcash has strong privacy features, but many people still use its transparent mode, which weakens its overall anonymity.
Trade-offs between privacy and transparency
Privacy coins protect anonymity but have downsides:
- Regulatory issues: Many exchanges restrict or ban privacy coins.
- Limited adoption: Fewer businesses accept them compared to Bitcoin.
- Higher fees: Privacy features make transactions larger, increasing costs.
- Exchange restrictions: Some platforms require extra verification or don’t support them.
Bitcoin is easier to use but easier to trace. Privacy coins provide better anonymity, though they’re harder to access. If you want privacy, you must decide which trade-offs matter most.
Can Bitcoin become fully anonymous?
Bitcoin was never designed for complete privacy. Could that change?
Current limitations in Bitcoin privacy
Bitcoin’s biggest privacy challenge is its open and permanent transaction history. Once a wallet address is linked to a person, all past and future transactions can be traced. Even those who take extra precautions can still be exposed.
Key limitations include:
- Public transaction records: Bitcoin is traceable to anyone, so people can easily follow Bitcoin movements.
- Wallet address reuse: Using the same address multiple times makes it easier to link transactions to a real-world identity.
- Exchange regulations: Most crypto exchanges require identity verification, meaning Bitcoin bought or sold on these platforms is no longer private.
- Blockchain forensic analysis: Companies specializing in Bitcoin forensic analysis use sophisticated tracking methods to cluster wallet addresses and uncover identities.
Emerging privacy technologies for Bitcoin
Developers continue working on ways to improve Bitcoin’s privacy. Some of the most promising developments include:
- Taproot: Makes multi-signature transactions indistinguishable from regular transactions, reducing visibility on the blockchain.
- Lightning Network: A second-layer payment solution that allows people to transact off-chain, keeping transactions out of the public ledger.
- PayJoin (P2EP): A CoinJoin variation where both the sender and receiver contribute inputs to a transaction, breaking common tracking heuristics.
- Stealth addresses: One-time addresses that prevent transactions from being linked to a single wallet.
These technologies help, but they don’t completely eliminate traceability. If someone cashes out Bitcoin through a regulated exchange or interacts with a traceable address, their identity can still be uncovered.
The future of Bitcoin anonymity
Bitcoin may never be as private as Monero or Zcash, but ongoing developments aim to improve its privacy. Future updates could make tracking transactions more difficult, even if full anonymity remains out of reach.
Stronger mixing techniques may help obscure transaction histories by making it harder to link inputs and outputs. Wider adoption of the Lightning Network could enhance privacy by allowing more transactions off-chain and keeping them out of the public ledger. Decentralized, privacy-focused exchanges may also reduce reliance on identity verification, giving people more control over their financial privacy.
Ethical and legal considerations of Bitcoin traceability
Governments continue to tighten regulations, especially around privacy coins and Bitcoin mixers. This further fuels the debate over crypto anonymity.
Law enforcement vs. financial privacy
Law enforcement agencies use Bitcoin’s traceability to investigate crimes like money laundering, fraud, and ransomware. Blockchain analysis helps track illicit funds, seize stolen Bitcoin, and identify criminals. The FBI’s recovery of the Colonial Pipeline Bitcoin ransom shows how effective these tools can be.
Financial privacy advocates see this as overreach. Wanting to keep transactions private doesn’t mean someone is engaged in illegal activity. They argue that people should be able to spend money without government surveillance, just like with cash.
This creates a privacy vs. security dilemma. Regulators view transparency as a way to stop financial crime, while others worry that excessive oversight could lead to censorship and loss of financial freedom.
Regulations on privacy coins and mixing services
Governments are cracking down on privacy-enhancing tools. Some have restricted or banned privacy coins like Monero and Zcash, while others have removed them from exchanges.
Bitcoin mixers face even stricter regulations. Mixers are often labeled as money laundering tools. Several have been shut down, including ChipMixer and Blender.io, accused of processing illicit funds.
Key regulatory actions include:
- U.S. Treasury sanctions against Tornado Cash, an Ethereum-based mixer, for alleged criminal use.
- EU proposals to restrict anonymous crypto transactions, making privacy wallets and mixers harder to use.
- Crypto exchanges delisting Monero, Zcash, and Dash, limiting access to privacy-focused cryptocurrencies.
The ongoing debate over crypto anonymity
The fight between financial privacy and regulation isn’t going away. Governments push for stricter oversight, while privacy advocates and developers create tools to protect anonymity.
Some argue complete anonymity enables crime, yet others warn that a cashless world without privacy tools exposes people to financial surveillance.
As regulations tighten, those seeking private transactions may turn to decentralized exchanges, privacy wallets, and second-layer solutions like the Lightning Network. However, as governments crack down on these options, maintaining crypto privacy becomes increasingly difficult.
FAQs on Bitcoin traceability and privacy
Can Bitcoin transactions be traced?
Yes, every Bitcoin transaction is recorded on a public blockchain. While wallet addresses don’t include names, forensic tools can link them to real people. Exchanges that require ID, reused addresses, and spending habits make tracking easier. Law enforcement and blockchain analysts use these methods to trace stolen funds and monitor activity. Bitcoin offers some privacy, but it’s not anonymous.
How can I make my Bitcoin transactions more private?
Use new wallet addresses for each transaction. Privacy tools like CoinJoin, Bitcoin mixers, and stealth addresses help break transaction trails. The Lightning Network keeps payments off the main blockchain. Privacy wallets like Wasabi and Samourai add extra protection. Avoid using regulated exchanges that require identity verification.
What are the best privacy coins for anonymity?
Monero and Zcash offer better privacy than Bitcoin. Monero hides senders, receivers, and amounts by default. Zcash lets people choose private or transparent transactions. Other options like Dash and Firo have built-in privacy features. Unlike Bitcoin, these coins are designed to prevent tracking. However, some exchanges limit access due to regulations.
Does using a VPN or Tor improve Bitcoin privacy?
A VPN or Tor hides your IP address when making Bitcoin transactions. This prevents websites and exchanges from logging your location, but it doesn’t stop blockchain analysis from tracking funds. If a wallet address is linked to you, your transactions remain visible. For better privacy, use a crypto VPN or Tor alongside CoinJoin or privacy wallets.

30-day money-back guarantee



























Who is owner of this account
Lexie wrote this post for ExpressVPN.
ME COMPJUTER
very good post thanks Bitcoin
FOR MI